

Novel approaches for robust decoding
High decoding accuracy is necessary not only for BCI but also for neural representation analysis. However, due to individual variance of EEG signals, even popular techniques such as ERD and visually evoked potentials are not robust enough, and some sort of people cannot show enough accuracy. Through international collaboration, I have contributed to developing two novel methods that can enhance the decoding accuracy of movement prediction estimation. In Ganesh et al., (Science Advances, 2018), we have developed a method to detect motion intention relying on testing the internal forward model people develop prior to movements. This novel method can reduce the decoding time to 100ms, where conventional approaches require about 1s (Fig.1). This is significant as this would promise real-time control of e.g. robots. Furthermore, this approach is robust since it was detected even from people who have not shown a clear ERD phenomenon. In another project (Minati et al., Chaos, 2019), we have developed a novel method based on phase-locking value (PLV) describing the phase difference between the frequency components of EEG signals corresponding to different movements. By simply adding amplitude information to PLV, we could increase accuracy by 7% in over 100 subjects (Figs. 2, 3).

Fig. 1. Fast and accurate decoding
based on motor prediction error (Ganesh et al., Science Advances, 2018).
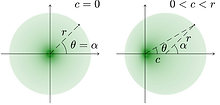
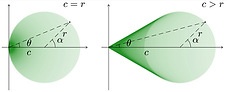
Fig. 2. Enhancement of difference
after adding amplitude information (Minati et al., Chaos, 2019).
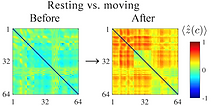
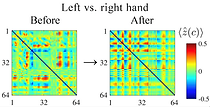
Fig. 3. The enlargement of the difference in EEG signals between two movements. (Minati et al., Chaos, 2019).